Definition and Function of Wall Claddings
Wall claddings refer to the layer of material covering the exterior or interior walls of a building, typically used to enhance the building's appearance while providing additional protection. Their function extends beyond aesthetic enhancement to include waterproofing, thermal insulation, wind resistance, and sound insulation. The choice of wall cladding directly impacts the building's energy consumption, maintenance costs, and indoor comfort. Therefore, choosing the right cladding material is not only an aesthetic consideration in architectural design but also a guarantee of energy efficiency throughout the building's lifespan.
Common Wall Cladding Materials and Their Characteristics
Currently, there are many types of wall cladding materials available on the market, each with its unique advantages and applications. Choosing the right cladding material requires considering factors such as performance, cost, and durability.
1. Stone Cladding
Stone cladding, as a traditional and classic material, is still widely used in high-end buildings and commercial facilities due to its natural texture and durability. Stone has good weathering and corrosion resistance, effectively resisting the erosion of harsh weather. Common stones such as granite and marble not only have a natural and elegant appearance but also add a sense of solidity to the building. However, stone cladding is more difficult to install, requiring professional technicians, and is relatively expensive, making it more suitable for buildings that need to project a grand and high-end image.
2. Metal Cladding
With technological advancements, metal materials are increasingly used in the decoration of building exteriors. Aluminum alloys and stainless steel, due to their excellent weather resistance, oxidation resistance, and lightweight properties, have become popular choices in modern architectural design. Metal cladding not only provides a modern appearance but also offers excellent durability and wind resistance. Metal surfaces can undergo various treatments, such as spraying and anodizing, which not only enhance their aesthetics but also improve their corrosion resistance. Metal cladding is suitable for various building types, and is particularly prominent in high-rise buildings and commercial buildings.

3. Ceramic and Stone Cladding
Ceramic and stone materials are commonly used for the decoration of building facades. With their unique visual effects and excellent durability, they have become the preferred choice for many modern buildings. Ceramic materials have excellent high-temperature and acid-alkali resistance, making them widely used in the exterior walls of industrial buildings and commercial spaces. Stone, as a traditional wall decoration material, is durable and weather-resistant, suitable for low-rise buildings and residential areas. Although these materials are relatively expensive, their texture and long-term stability make them still important in some high-end projects.
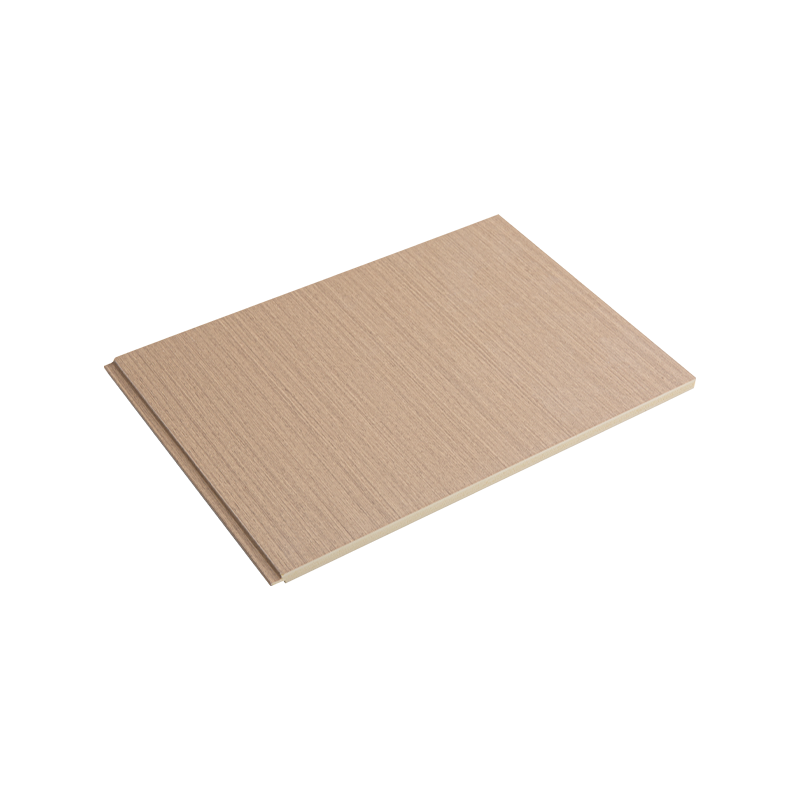
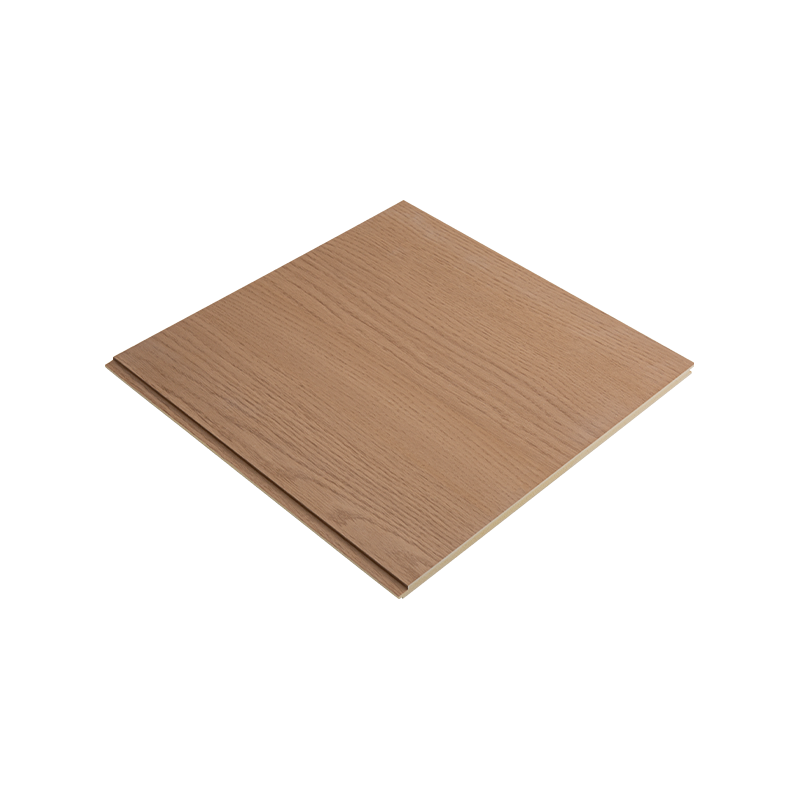
4. Wooden Cladding
Wooden wall cladding, as a combination of nature and modernity, is gradually becoming an indispensable decorative element in high-end residential and commercial buildings. Wood not only brings a warm and natural atmosphere but also has good thermal insulation and moisture absorption properties, helping to improve indoor humidity and temperature balance. Finely processed and treated wood can have good weather resistance and durability, suitable for use in mild climates. However, because wood is susceptible to moisture, insect infestation, and other natural factors, regular maintenance is required to ensure its long-term performance.
5. Composite Material Cladding
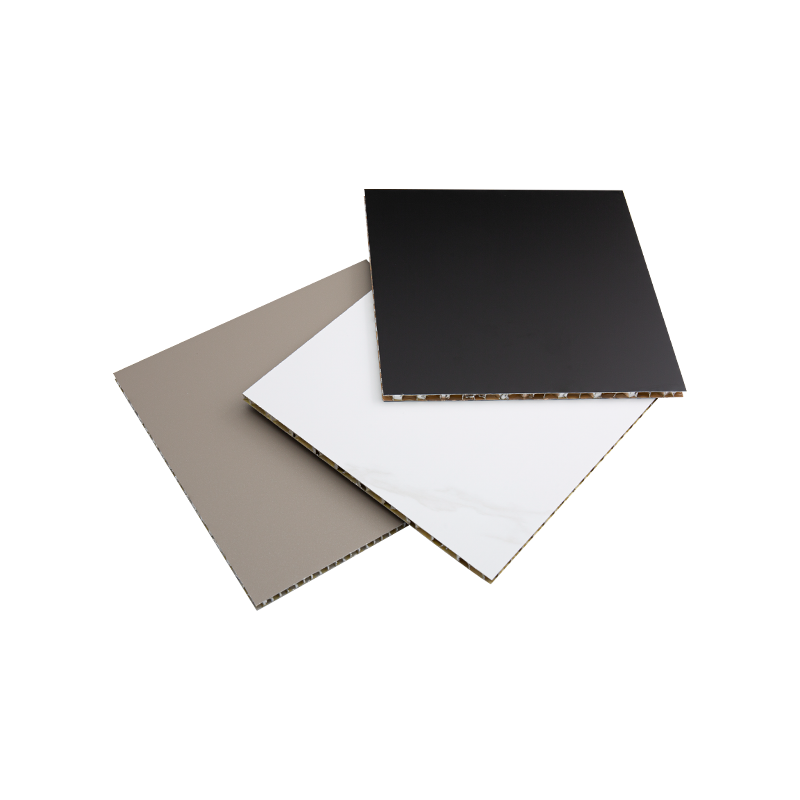
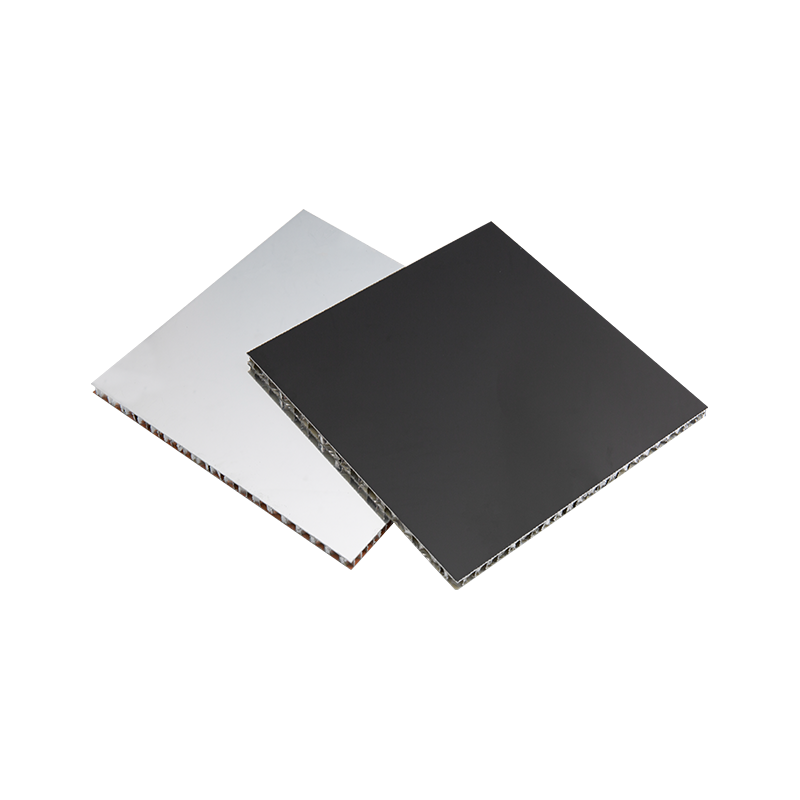
Composite material cladding combines the advantages of various materials, possessing good mechanical properties and low self-weight. Common composite materials include aluminum composite panels and glass fiber reinforced plastics (GRP). These materials not only have a modern appearance but also possess good weather resistance and corrosion resistance, making them very suitable for large-scale commercial buildings, office buildings, and other places. Composite materials are usually lightweight, easy to construct, and have a short construction period, therefore, they are widely used.
How to Choose the Right Wall Cladding Material
When choosing wall cladding materials, designers need to consider various factors, including the building's geographical location, function, budget, and aesthetic requirements. For example, buildings located in high-humidity or high-temperature areas should prioritize materials with strong weather resistance and corrosion resistance; while for projects pursuing a modern and personalized design, metal or composite material cladding might be a better choice. In addition, the sustainability and environmental performance of materials are increasingly important factors, and many construction projects are beginning to favor environmentally friendly and recyclable materials.
Wall Cladding Maintenance and Care
Wall cladding is not only a display of the building's appearance but also a guardian of the building's health. Therefore, regular maintenance and care are crucial for extending the lifespan of wall cladding. Different materials have different maintenance needs. For example, although metal cladding has strong corrosion resistance, it still requires regular cleaning to prevent pollutants from accumulating over time. Stone and wood materials require more meticulous maintenance, especially in areas with high humidity, where moisture and mold prevention measures are particularly important.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Wall Cladding
Q1: What are the main functions of wall cladding?
Wall cladding has multiple functions, including aesthetics, protection, insulation, and soundproofing. It not only enhances the design of the building's exterior but also effectively protects the walls from external environmental influences, increasing the building's lifespan.
Q2: What are some common wall cladding material options?
Common wall cladding materials include stone, metal, ceramic, wood, and composite materials. Each material has different characteristics and applications, and designers need to choose the most suitable material based on the building's actual needs.
Q3: How to choose the right wall cladding material?
When choosing wall cladding materials, in addition to considering the aesthetics of the building, it is necessary to comprehensively evaluate factors such as weather resistance, maintenance costs, environmental performance, and budget to ensure long-term effectiveness.
Q4: How difficult is wall cladding maintenance?
The difficulty of wall cladding maintenance varies depending on the material. Metal materials are generally easier to maintain, while natural materials such as stone and wood require more careful attention, especially in humid or extreme climates.
Q5: How long is the lifespan of wall cladding?
The lifespan of wall cladding is closely related to the chosen material, construction quality, and subsequent maintenance. Typically, high-quality stone, metal, and composite wall coverings can last for decades, while wood and ceramic materials have a shorter lifespan and require regular maintenance.
Wall coverings, as an important component of architectural design, not only give buildings a unique appearance but also improve their functionality and comfort. When choosing wall covering materials, designers should consider various factors such as material performance, cost, and maintenance requirements to make informed decisions based on the specific needs of the project.
 English
English عربى
عربى русский
русский